Want to know more about the 16 bit vs 24-bit recording?
Don’t worry! We will give you comprehensive guidance to distinguish them. There is a preferable option as well.
Let’s read on to discover?
Comparison between 16 bit vs 24-bit recording:
#1. Bit depth
First, let’s get to know the term “bit depth”.
Bit depth is the number of bits required to record audio. The way to think of it is as a set of levels in which we may split the audio energy.
There are 65,536 potential levels in 16-bit audio. The number of layers doubles with every increase in resolution. Meanwhile, we really have 16,777,216 levels when we go for 24 bit.
When you consider the number of levels accessible, the gap between 16-bit and 24-bit appears to be enormous.
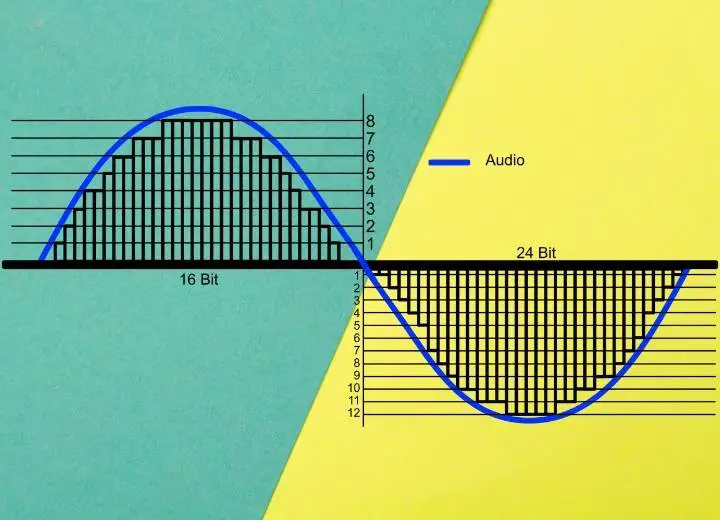
The bit depth of 16 bit vs 24 bit
#2. Bits and bytes
Digital data will transfer in bytes instead of individual bits during the recording process. A byte contains 8 bits. That figure is a digital word. This is why, in the digital age, everything is divisible by eight.
As a result, 16 bits equaled two bytes and 24 bits equaled three bytes. Both 16 and 24 bits have become standard since each indicates the next digital word.
#3. Sampling rate
The sampling rate is the frequency of sampling the analog audio wave’s amplitude. Let’s have a look at some instances to see what the rates mean.
44.1 kHz means sampling the analog audio 44,100 times per second. The Red Book CDs are an outstanding product that applies a 44.1 kHz sampling rate.
Another example is the 7.1 channel audio in DVDs and Blu-Rays. It uses a 96KHz sampling frequency, which samples the amplitude 96,000 times per second.
192 kHz is also a popular sampling rate. It samples 192,000 times per second for the MQA and high-definition music files.
Is there any difference between 16 bit and 24 bit recording in terms of sampling rate?
There are 65,536 samples in a 16-bit recording. A 24-bit recording, on the other hand, contains 16,777,216 samplings.
The gap is quite large here. A 24-bit recording offers 256 times the variety of possible amplitude changes as a 16-bit recording.
The potential resolution increases as the number of bits and sample rate utilized in quantization increases. Each second, a 16-bit 44.1KHz Red Book CD contains 28,901,376 possible sample points (44,100 x 65,536).
Can you calculate the number in a 24-bit 44.1kHz? It must be 44,100 x 16,777,216. Wow! The difference is not small at all.
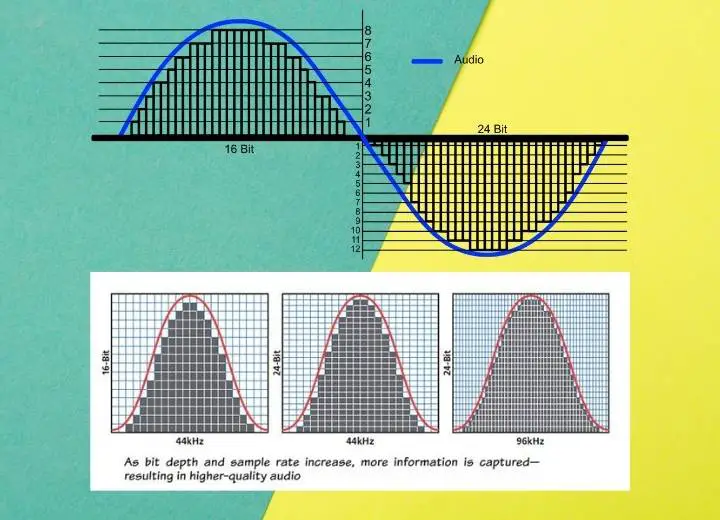
Sample rate examples
#4. Dynamic range
Dynamic range is the loudness difference between the weakest and strongest passages. Its measurement is decibels (dB).
One bit equals 6 dB. So, 16-bit has a dynamic range of about 96dB. The figure in 24-bit is 144dB.
In fact, we couldn’t identify the difference between 24-bit music and 16-bit versions of the identical files. That is the reason you may confuse the two audios when simply listening.
#5. Noise floor
The dynamic range isn’t the sole consideration. Regardless of what bit-depth the manufacturer claims your DAC decodes, the noise floor will also determine the Least Significant Bits (LSB) at the output of the DAC.
The noise floor will show the quietest sound that you can hear. The voltage of the LSB on your recording must be louder than the noise floor of the studio and the tools if you wish to hear it.
The noise floor voltage for 16-bit LSB is 76uV. The voltage for 24-bit LSB is lower: at 0.3uV.
It means that using 24-bit allows you to listen to your audio clearer.
What Should We Use?
After comparing some factors, you may know the differences. However, can you decide which one to use?
In terms of recording, choose the 24-bit option. This is true regardless of what you’re capturing. The difference will be noticeable if you have a decent microphone and a competent preamp. Preparing a clean audio system and highly dynamic instruments will enhance the quality of your product.
But, it is not as if having 24 bits of data improves the sound quality. Actually, it doesn’t.
We have discussed numbers and computations, not analog waveforms. Do you remember that?
It is possible to record very dynamic music using 24 bits of data demarcating your recording medium. It also includes very quiet, soft parts and extremely loud portions. Quiet sections will be less likely to struggle to keep above your system’s noise floor.
It is possible to record without compression. With greater headroom, you can work at lower ranks. This allows converters to relax.
Your instruments will sound crisper, and the vocals may sound cleaner. Hence, the song will blend better. There will be less noise since you are not exceeding the limitations of your capacity. So, 24-bit recordings do not sound better.
In reality, they may sound just as good as 16 bit. You can try to distinguish them here.
However, 24 bits provides the recordist with enough noise, floor, and headroom to make a great recording. It is a tool. In the proper hands, it can completely transform your audio experience.
Conclusion
After the comparison, you may know all about the distinction between 16 bit vs 24-bit recording.
Although their features differ a lot, their sound shares the same characteristics. 24 bit does not really outweigh the 16 bit.
However, 24-bit recording serves your project as a sound assistant. Just pick the 24-bit option if you can.
Hopefully, you find the article helpful!
